What should I pay attention to when mixing paint colors?
In addition to the protective function, another important function of paint is the decorative role. Different colors of paint add great commercial value to industrial products. The color of paint is increasingly valued by manufacturers and users. A good color mixer can quickly and accurately mix the target color, thus improving production efficiency, reducing color differences between batches, stabilizing product quality and improving product competitiveness.
How to quickly and accurately mix the color of paint depends on the understanding of color and experience. There are various methods, several of which are shared today.
1. Properties of colors and color mixing methods
The properties of color are hue, brightness and purity. Hue is the appearance of the color characteristics, also called hue; brightness refers to the degree of light and darkness of the color; purity is also called saturation or color, that is, the degree of vividness of the color. The purity of the original color is the highest, followed by the inter-color, the lowest complex color. Whether the brightness is raised or lowered, the hue and purity will change. The essence of color mixing is to make the 3 parameters of color consistent with the sample color. The color mixing of paint is based on the subtractive principle. The color mixing method simply means: what is missing is added, and what color is more is added to this color.
2. the influencing factors of visual color comparison
Size: the same specimen coated in different sizes of the test plate shows the difference in color. As can be seen from Figure 1, the same color, small area of the color visually no area of large vivid, bright. Analysis of the reason may be a large area of light reflected to the human eye more, so it looks more vivid, more bright, which is the area effect. So in the visual colorimetric test plate and the size of the standard plate consistent. The correct method of plate making is to dilute the specimen to the proper viscosity and then paint it quickly and evenly along the vertical and horizontal directions. When spraying, the gun is about 20cm away from the painted surface between, moving at an even speed, with air pressure of 0.2~0.4MPa.
Area size color comparison
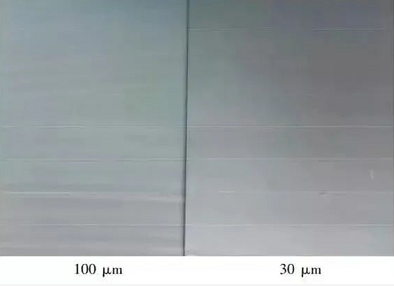
In addition the viscosity of the specimen has a great influence on the thickness of the coating film, the viscosity is too large to make the test plate leveling is not good, affecting the color reflection. The effect of coating film thickness on color is shown in Figure 2.
Color comparison of different thickness of coating film
From Figure 2, we can see that the color of the test plate with thickness of 100μm is darker. Analysis of the reason may be that the thicker coating film real dry slower, carbon black and phthalocyanine blue floating color time is longer thus leading to darker color after drying. In addition to the size, the area of the item is also an indispensable characteristic of color. In the design often occurs although the color with more suitable, but because of the color area size, color shape, color position and other poor control and make the visual effect of the situation greatly reduced. Usually, the color design of large areas choose more brightness, low color, contrast weak color, to bring people a bright, lasting and harmonious comfort, such as architecture, indoor ceiling, walls, booths. Medium area of the color more with a medium degree of contrast, such as clothing color matching, neighboring color groups and brightness in the tone contrast is used more, both to arouse visual interest, but not excessive stimulation. Small areas of color commonly used bright colors and bright colors and strong contrast, such as small goods, small signs, etc., the purpose is to make people fully attention.
Direction: Colors have directionality and can look very different from different angles. Especially for metallic paints, the difference is greater from different angles. This may be because different objects have different ability to reflect light, and metal has high reflectivity of light, and the angle is different, the difference of light entering human eyes is greater. The national standard GB/T9761-1988 stipulates that the method of visual colorimetry is vertical observation with an angle of incidence of 0° and a distance of 50cm from the sample.
Environment: The color of the surrounding environment has a great impact on visual colorimetry. Because the light reflected from the surrounding objects will be part of the light source to the measured object, which is equal to the color of the light source has changed, thus causing errors in color judgment. So the visual colorimetric environment in addition to the experimental plate should not be other bright colors, color matching personnel should not wear brightly colored clothes.
3. color mixing should pay attention to the problem
Resin compatibility: When mixing colors, choose the same resin system or color paste, if the compatibility is not good, there will be precipitation, delamination and even gelation. For example, if the epoxy color paste is used for color mixing, the epoxy resin will precipitate out and affect the fineness of the product. Water-based alkyd paint color mixing must not use alkyd paint color paste. Experience shows that adding 1% of alkyd paint coloring paste to water-based alkyd paints will cause white floating, and the more you blend the color, the lighter the color phenomenon. Analysis of the reason may be that the alkyd lacquer oil degree is longer, weaker polarity, and water-based alkyd resin compatibility is poor, and blending paint color paste into the system, the pigment and blending paint resin separation and cohesion sink into the lower layer, resulting in white floating, as shown in Figure 3.
Before and after whitening comparison
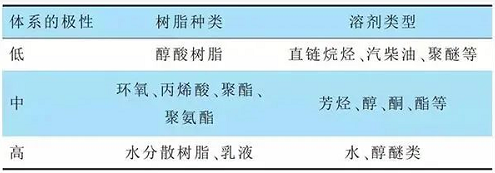
The solvent system of color paste has great influence on the finished product. If the solvency power of the solvent is too poor, it will cause the color paste to be unstably dispersed in the resin, which may cause delamination, precipitation, flocculation or even scrap in serious cases. If the solvency power is too strong, it may produce bottom biting or color bleeding to the primer with it. The choice of solvent depends on the type of resin and the polarity of the system. The selection of solvents is based on Table 1.
The impact of auxiliary raw materials: when mixing colors, we should consider the impact of dry materials, curing agents and other raw materials on the color, dry materials are darker and have a greater impact on the color of white and other light-colored paint. Epoxy amine curing agent color is darker, the amount is also larger more attention should be paid. There are also industrial paints with polyamide wax to prevent sinking and hanging, but the addition of polyamide wax will affect the normal floating color of pigments, and the color will be slightly lighter than when it is not added; if it is used in silver powder paint, it will affect the floating type of silver powder, which may cause the silver powder paint is not white enough. The fineness of the color paste is too high to affect the utilization rate of the pigment, and also affect the appearance of the coating film, and in the storage process, it will also cause discoloration or even affect the use of the pigment flocculation, and the fineness of the color paste is generally controlled below 20μm in actual production. The viscosity of the color paste is too high and not easy to disperse, the pigment is not sufficiently spread, which will cause the waste of pigment; but the color paste is too thin, the pigment content is low, it may need more color paste, at the same time, it will bring in the components other than pigment, such as resin or solvent, which will have certain influence on the gloss of the coating film.
Surface drying time: The wet color of paint is generally lighter and becomes darker after drying, but there are differences in different systems. The difference between wet and dry colors of water-based paints is large, as shown in Figure 4.
The alkyd blending class is the next best, and the difference between nitro, acrylic, epoxy and polyurethane classes is smaller. Because the surface drying time of nitro, acrylic, epoxy and polyurethane is short, the black and blue colors have dried up before they have time to float on the surface. The water-based alkyd and alkyd blending class is slow to dry, and the black and blue pigments that are easy to float have a long time to float, so the color is darker after drying.
The influence of surfactant: when preparing compound color paint, because of the variety of pigments, the difference of oil absorption, density and particle size may cause floating color, usually floating white, floating blue, floating yellow, etc.. It can be improved by adding appropriate amount of dispersant (Deqian 904S, Deqian 983, etc.) anti-floating agent, the dosage is 0.1%~0.5%. The variety and dosage of surfactant should be decided by experiment according to different resin systems and different pigments.
Complementary color use: complementary color use should pay attention to the very bright colors must not use complementary color. The color is bright because the saturation of the color is relatively high, which is commonly known as high color color, after the complementary color produces black, the color color color is reduced, the gray content increases, and the color looks darker.
Pigment selection and matching: The selection of pigment should be based on and applicable to the use of paint. If it is used in outdoor, we must choose sunlight resistant pigment, if it is used as primer or indoor, we may not consider the sunlight resistance of pigment.
To make a brighter purple, you must choose permanent purple, not red and blue with it. Although big red powder and phthalocyanine blue will produce more purple color, but the yellow phase in big red will be complementary with purple to produce black, thus making purple dark; in addition, big red is also easy to float, and the effect of opening cans is poor. As for iron red can not be used, first of all, iron red itself is darker, it is impossible to make a more vivid color; secondly, iron red inside the red less, and blue will produce a small amount of purple, but the purple produced will be consumed by the iron red own yellow left little. So do not use iron red and phthalocyanine blue with the color of the purple phase, because the red inside the iron red is less, and the blue can not produce too much purple will only make the color darker. Gray if the blue phase is heavy, you can use iron red and then add the right amount of yellow to offset the blue phase.
To do more fresh green, preferred phthalocyanine green, do not use yellow-blue with. Because phthalocyanine blue generally shows blue-violet phase, although the purple color is not much, but still will be complementary with yellow to make the color darker; In addition, light yellow and medium yellow show red phase, the green and yellow pigment with yellow-blue complementary will make the green darker. You can use blue pigment with a yellow head and yellow pigment with a green head (lemon yellow) to match the color.
Orange is usually matched with red and yellow, but to make a brighter orange, you must not use lemon yellow. Because lemon yellow shows green phase, green and red complement each other will make the color darker. Do not choose blue-phase red (such as purple-red), because the red-yellow orange and purple-red inside the blue complementary will make the color darker. Should be selected with red head of yellow (such as medium yellow and light yellow) and with yellow head of red (such as molybdenum-chromium red, big red, etc.).
Aluminum powder paint: there are flash silver, aluminum powder, pearl powder paint, color mixing must choose transparent color paste to ensure the metal effect. Flash silver, aluminum powder, pearl powder color, shape, particle size should be carefully screened, but also in advance in the solvent wetting dispersion before adding to avoid affecting the fineness. Should also consider the hammering agent, floating flower agent and other additives and the amount of the impact on the texture of the coating film.
Water-based paint: In the water-based system, the wetting ability of the resin on the pigment is worse than that of the solvent-based, and it is easy to see that the color is discolored after storage for a period of time. The analysis may be that different resins in the system have different wetting ability to the pigment, and after the color paste enters the system, various resins in the system start to fight for the pigment. The pigment is separated from the resin in the color paste and combined with the resin with better wettability in the system to enhance the color spread and the color becomes darker; on the contrary, if the pigment is flocculated after separation, it will cause the color to become lighter. The use of resin-free color paste can solve the problem of color change. After entering the system, the pigment and the resin in the system can freely choose the best combination, and the system will be more stable and not easy to change color.
Although many paint manufacturers now have computer color mixing, but because of the computer color mixing on the stability of color masterbatch dependence; on the gloss of different, surface texture of the coating color measurement error is relatively large; on the curved surface, shaped workpiece can not be measured color; matte, no light system color matching is not accurate enough, so the paint color mixing work, the final or manual to complete. The colorist needs to continuously accumulate, summarize and improve, in order to better complete the color mixing work of paint.
UV coating raw materials : UV Monomer Same series products
| Polythiol/Polymercaptan | ||
| DMES Monomer | Bis(2-mercaptoethyl) sulfide | 3570-55-6 |
| DMPT Monomer | THIOCURE DMPT | 131538-00-6 |
| PETMP Monomer | PENTAERYTHRITOL TETRA(3-MERCAPTOPROPIONATE) | 7575-23-7 |
| PM839 Monomer | Polyoxy(methyl-1,2-ethanediyl) | 72244-98-5 |
| Monofunctional Monomer | ||
| HEMA Monomer | 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate | 868-77-9 |
| HPMA Monomer | 2-Hydroxypropyl methacrylate | 27813-02-1 |
| THFA Monomer | Tetrahydrofurfuryl acrylate | 2399-48-6 |
| HDCPA Monomer | Hydrogenated dicyclopentenyl acrylate | 79637-74-4 |
| DCPMA Monomer | Dihydrodicyclopentadienyl methacrylate | 30798-39-1 |
| DCPA Monomer | Dihydrodicyclopentadienyl Acrylate | 12542-30-2 |
| DCPEMA Monomer | Dicyclopentenyloxyethyl Methacrylate | 68586-19-6 |
| DCPEOA Monomer | Dicyclopentenyloxyethyl Acrylate | 65983-31-5 |
| NP-4EA Monomer | (4) ethoxylated nonylphenol | 50974-47-5 |
| LA Monomer | Lauryl acrylate / Dodecyl acrylate | 2156-97-0 |
| THFMA Monomer | Tetrahydrofurfuryl methacrylate | 2455-24-5 |
| PHEA Monomer | 2-PHENOXYETHYL ACRYLATE | 48145-04-6 |
| LMA Monomer | Lauryl methacrylate | 142-90-5 |
| IDA Monomer | Isodecyl acrylate | 1330-61-6 |
| IBOMA Monomer | Isobornyl methacrylate | 7534-94-3 |
| IBOA Monomer | Isobornyl acrylate | 5888-33-5 |
| EOEOEA Monomer | 2-(2-Ethoxyethoxy)ethyl acrylate | 7328-17-8 |
| Multifunctional monomer | ||
| DPHA Monomer | Dipentaerythritol hexaacrylate | 29570-58-9 |
| DI-TMPTA Monomer | DI(TRIMETHYLOLPROPANE) TETRAACRYLATE | 94108-97-1 |
| Acrylamide monomer | ||
| ACMO Monomer | 4-acryloylmorpholine | 5117-12-4 |
| Di-functional Monomer | ||
| PEGDMA Monomer | Poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate | 25852-47-5 |
| TPGDA Monomer | Tripropylene glycol diacrylate | 42978-66-5 |
| TEGDMA Monomer | Triethylene glycol dimethacrylate | 109-16-0 |
| PO2-NPGDA Monomer | Propoxylate neopentylene glycol diacrylate | 84170-74-1 |
| PEGDA Monomer | Polyethylene Glycol Diacrylate | 26570-48-9 |
| PDDA Monomer | Phthalate diethylene glycol diacrylate | |
| NPGDA Monomer | Neopentyl glycol diacrylate | 2223-82-7 |
| HDDA Monomer | Hexamethylene Diacrylate | 13048-33-4 |
| EO4-BPADA Monomer | ETHOXYLATED (4) BISPHENOL A DIACRYLATE | 64401-02-1 |
| EO10-BPADA Monomer | ETHOXYLATED (10) BISPHENOL A DIACRYLATE | 64401-02-1 |
| EGDMA Monomer | Ethylene glycol dimethacrylate | 97-90-5 |
| DPGDA Monomer | Dipropylene Glycol Dienoate | 57472-68-1 |
| Bis-GMA Monomer | Bisphenol A Glycidyl Methacrylate | 1565-94-2 |
| Trifunctional Monomer | ||
| TMPTMA Monomer | Trimethylolpropane trimethacrylate | 3290-92-4 |
| TMPTA Monomer | Trimethylolpropane triacrylate | 15625-89-5 |
| PETA Monomer | Pentaerythritol triacrylate | 3524-68-3 |
| GPTA ( G3POTA ) Monomer | GLYCERYL PROPOXY TRIACRYLATE | 52408-84-1 |
| EO3-TMPTA Monomer | Ethoxylated trimethylolpropane triacrylate | 28961-43-5 |
| Photoresist Monomer | ||
| IPAMA Monomer | 2-isopropyl-2-adamantyl methacrylate | 297156-50-4 |
| ECPMA Monomer | 1-Ethylcyclopentyl Methacrylate | 266308-58-1 |
| ADAMA Monomer | 1-Adamantyl Methacrylate | 16887-36-8 |
| Methacrylates monomer | ||
| TBAEMA Monomer | 2-(Tert-butylamino)ethyl methacrylate | 3775-90-4 |
| NBMA Monomer | n-Butyl methacrylate | 97-88-1 |
| MEMA Monomer | 2-Methoxyethyl Methacrylate | 6976-93-8 |
| i-BMA Monomer | Isobutyl methacrylate | 97-86-9 |
| EHMA Monomer | 2-Ethylhexyl methacrylate | 688-84-6 |
| EGDMP Monomer | Ethylene glycol Bis(3-mercaptopropionate) | 22504-50-3 |
| EEMA Monomer | 2-ethoxyethyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate | 2370-63-0 |
| DMAEMA Monomer | N,M-Dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate | 2867-47-2 |
| DEAM Monomer | Diethylaminoethyl methacrylate | 105-16-8 |
| CHMA Monomer | Cyclohexyl methacrylate | 101-43-9 |
| BZMA Monomer | Benzyl methacrylate | 2495-37-6 |
| BDDMP Monomer | 1,4-Butanediol Di(3-mercaptopropionate) | 92140-97-1 |
| BDDMA Monomer | 1,4-Butanedioldimethacrylate | 2082-81-7 |
| AMA Monomer | Allyl methacrylate | 96-05-9 |
| AAEM Monomer | Acetylacetoxyethyl methacrylate | 21282-97-3 |
| Acrylates Monomer | ||
| IBA Monomer | Isobutyl acrylate | 106-63-8 |
| EMA Monomer | Ethyl methacrylate | 97-63-2 |
| DMAEA Monomer | Dimethylaminoethyl acrylate | 2439-35-2 |
| DEAEA Monomer | 2-(diethylamino)ethyl prop-2-enoate | 2426-54-2 |
| CHA Monomer | cyclohexyl prop-2-enoate | 3066-71-5 |
| BZA Monomer | benzyl prop-2-enoate | 2495-35-4 |