Apa saja monomer dan resin akrilat yang digunakan dalam pelapis logam UV?
Aplikasi pelapis UV untuk logam (DTM) memerlukan resin dengan keseimbangan sifat elastisitas dan ketangguhan untuk memastikan bahwa artikel dapat menahan kondisi yang menuntut kemampuan bentuk pasca-proses, termasuk goresan dan abrasi.
Selain itu, lapisan akhir harus sesuai untuk berbagai jenis logam yang mungkin memiliki kontaminasi permukaan yang dapat membuat adhesi menjadi sulit.
Presentasi
Pekerjaan ini akan menyelidiki hasil kinerja monomer dan oligomer akrilat ketika diuji melalui aplikasi penggunaan akhir yang khas, terutama mengukur fleksibilitas dan karakteristik adhesi pelapis.
Zwitterion dengan sifat yang mempromosikan adhesi akan diuji sendiri atau dikombinasikan dengan promotor adhesi fungsional monomer asam untuk menentukan jenis zwitterion terbaik untuk substrat tertentu. Tingkat penambahan promotor adhesi yang tepat juga akan ditentukan untuk mendapatkan hasil performa terbaik. Selain itu, ketahanan kelembaban dalam kaitannya dengan jenis oligomer akan dieksplorasi.
Perkembangan signifikan lainnya dalam industri pembuatan kaleng adalah penghapusan Bisphenol A (BPA) dari pelapis yang digunakan dalam kemasan makanan. Keunggulan kinerja oligomer poliester akrilat dibandingkan BPA epoksi akrilat sangat luar biasa. Masing-masing formulasi yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini hampir bebas BPA.
Eksperimen
Untuk pelapis yang dapat disembuhkan dengan radiasi untuk logam, diperlukan kriteria ketahanan gores dan abrasi yang biasa. Namun demikian, tugas ini menantang, karena pelapis ini perlu diaplikasikan pada berbagai substrat logam dengan sifat permukaan yang berbeda yang dapat memengaruhi adhesi. Selain itu, jika pelapis ini digunakan untuk kaleng dan kemasan yang kaku, tidak hanya diperlukan daya rekat, tetapi juga diperlukan tingkat fleksibilitas untuk menahan proses ketat yang terlibat dalam pembuatan wadah logam jadi. Ketahanan panas dan kelembaban juga merupakan faktor ketika mempertimbangkan proses distilasi yang terkait dengan kemasan makanan atau jika pipa yang dilapisi akan digunakan di luar ruangan.
Untuk memenuhi persyaratan yang sulit ini, dua jenis produk telah dikembangkan. Yang pertama adalah serangkaian monomer ester fosfat, yang digunakan sebagai aditif. Mereka berkisar dalam kelompok fungsional dari mono hingga tri-fungsional dan memiliki nilai asam yang berbeda. Untuk kepentingan diskusi, mereka digambarkan sebagai monomer fungsional asam atau AFM.
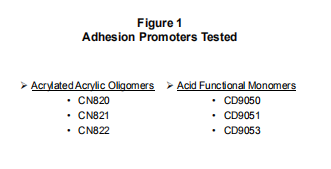
. Kelompok kedua paling baik digambarkan sebagai zwitterion akrilik fungsional berbobot molekul tinggi yang memiliki promotor adhesi yang bereaksi dengan rantai utama. Oligomer bersifat bifungsional dan untuk adhesi optimal, komposisi akhir harus 30-50%. Untuk memudahkan diskusi, disarankan agar komponen ini disebut sebagai adhesi yang mempromosikan oligomer atau APO. Daftar komponen ini disediakan pada Gambar 1.
Application and Curing Conditions
The conditions chosen here represent those commonly used in the metal decorating industry. The ideal film thickness should be kept to a minimum cost, but at the same time be thick enough so that performance is not compromised. This is achieved at the nominal film thicknesses listed below. In addition, the curing conditions quoted are fairly common for these applications, as the application of thin transparent layers does not require special light sources. The type of radiometer and the results obtained are also reported to avoid any variation in conditions that would affect the film properties, thus ensuring consistency of the end-use test results. Figure 2 depicts the application curing conditions.

Bisphenol A Free Formulation Options
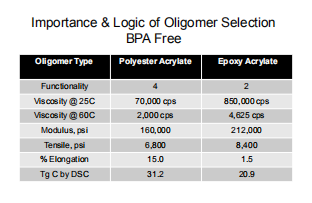
Bisphenol A (BPA) is an important raw material used primarily in the manufacture of epoxy resins. With excellent toughness, adhesion, moldability and chemical properties, BPA epoxy acrylates have been a major oligomer for the coatings industry for many years. A recent study conducted by the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences expressed concern about the long-term health effects of BPA exposure. As a result, can manufacturers and formulators in the food packaging industry are moving toward a BPA-free system. The oligomers that meet the BPA-free criteria are polyester acrylates (PEAs). The table below provides a comparison of the physical properties of PEAs and epoxies and highlights the benefits of using BPA-free alternatives.
In addition to being BPA-free, PEAs have the following benefits.
1) Faster curing, four-functional compared to two-functional
2) Easier handling due to significantly lower viscosity of PEAs
3) More freedom in formulation as more PEAs can be used in the final formulation without adversely affecting viscosity
4) PEAs are as tough and more flexible as epoxy resins.
PEAs have better resistance to yellowing than BPA-based oligomers.
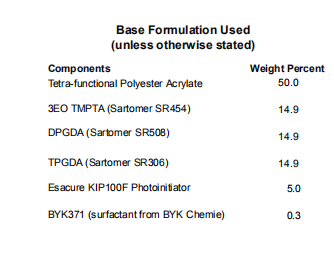
The formulation used for this study
As demonstrated above with obvious advantages, PEA was chosen as the main component of this formulation. The monomers selected for this study include tripropylene glycol diacrylate (TPGDA), dipropylene glycol diacrylate (DPGDA), and 3-ethoxytrimethylolpropane triacrylate (3EO-TMPTA).TPGDA is a low-volatility, low-viscosity monomer that is widely used in free radical polymerization for cost reasons.DPGDA is also an economical substitutable hexanediol diacrylate (HDDA) as a reactive monomer. It has good viscosity-reducing properties, is more user-friendly, and has a major irritation index (PII) of 2 compared to HDDA’s 5. Ethoxylated TMPTA was also selected for its low skin irritation, but it offers the added benefit of higher crosslinking and enhanced surface cure. The photoinitiator used for these formulations was polymerized alpha-hydroxyphenyl ketone mixed with 2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-phenyl-1 acetone. Surfactants are used to ensure proper wetting of the substrate. The viscosity of the base formulation is 300 cps @ 25°C.
Substrates used and end-use tests
All metal test panels used are from QPanel. before coating, the panels are cleaned with a solvent (MEK) to remove surface contamination. Substrates typically used for testing include aluminum (Alum), tinned steel (TPS) and cold rolled steel (CRS). The tests performed on the cured film are as follows. Cross-adhesion is chosen because it is related to the affinity of a given coating to the substrate. Reverse impact is interesting because it is not related to the adhesion of the coating but to the flexibility of the coating and provides an indication of the forming ability.MEK resistance gives a quick indication of the degree of curing of the coating.ASTM number references are given below.
1) Cross Bonding-ASTM D 3359
2) Reverse Impact Resistance-ASTM D 2794
3) Solvent Resistance-ASTM D 5402
Description of Acid Functional Monomers (AFMs)
As a family, these products can be described as acid esters. CD9050 (now SR9050) is a single-function tackifier monomer that provides excellent adhesion on metal substrates. CD9051 (SR9051) and CD9053 (SR9053) are three-functional versions of CD9050. They provide the same adhesion. However, because it is triple official, they offer faster cure response and greater hardness. These products are not recommended for use in fatty acids containing tertiary amines due to their high acid values. The recommended use level is 3% to 7%. Acid values range from 120 to 195 mg KOH/g. The following table illustrates the physical properties of the monomers.
UV Photoinitiator Same series products
| Product name | CAS NO. | Chemical name |
| Sinocure® TPO | 75980-60-8 | Diphenyl(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phosphine oxide |
| Sinocure® TPO-L | 84434-11-7 | Ethyl (2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl) phenylphosphinate |
| Sinocure® 819/920 | 162881-26-7 | Phenylbis(2,4,6-trimethylbenzoyl)phosphine oxide |
| Sinocure® 819 DW | 162881-26-7 | Irgacure 819 DW |
| Sinocure® ITX | 5495-84-1 | 2-Isopropylthioxanthone |
| Sinocure® DETX | 82799-44-8 | 2,4-Diethyl-9H-thioxanthen-9-one |
| Sinocure® BDK/651 | 24650-42-8 | 2,2-Dimethoxy-2-phenylacetophenone |
| Sinocure® 907 | 71868-10-5 | 2-Methyl-4′-(methylthio)-2-morpholinopropiophenone |
| Sinocure® 184 | 947-19-3 | 1-Hydroxycyclohexyl phenyl ketone |
| Sinocure® MBF | 15206-55-0 | Methyl benzoylformate |
| Sinocure® 150 | 163702-01-0 | Benzene, (1-methylethenyl)-, homopolymer,ar-(2-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-oxopropyl) derivs |
| Sinocure® 160 | 71868-15-0 | Difunctional alpha hydroxy ketone |
| Sinocure® 1173 | 7473-98-5 | 2-Hydroxy-2-methylpropiophenone |
| Sinocure® EMK | 90-93-7 | 4,4′-Bis(diethylamino) benzophenone |
| Sinocure® PBZ | 2128-93-0 | 4-Benzoylbiphenyl |
| Sinocure® OMBB/MBB | 606-28-0 | Methyl 2-benzoylbenzoate |
| Sinocure® 784/FMT | 125051-32-3 | BIS(2,6-DIFLUORO-3-(1-HYDROPYRROL-1-YL)PHENYL)TITANOCENE |
| Sinocure® BP | 119-61-9 | Benzophenone |
| Sinocure® 754 | 211510-16-6 | Benzeneacetic acid, alpha-oxo-, Oxydi-2,1-ethanediyl ester |
| Sinocure® CBP | 134-85-0 | 4-Chlorobenzophenone |
| Sinocure® MBP | 134-84-9 | 4-Methylbenzophenone |
| Sinocure® EHA | 21245-02-3 | 2-Ethylhexyl 4-dimethylaminobenzoate |
| Sinocure® DMB | 2208-05-1 | 2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl benzoate |
| Sinocure® EDB | 10287-53-3 | Ethyl 4-dimethylaminobenzoate |
| Sinocure® 250 | 344562-80-7 | (4-Methylphenyl) [4-(2-methylpropyl)phenyl] iodoniumhexafluorophosphate |
| Sinocure® 369 | 119313-12-1 | 2-Benzyl-2-(dimethylamino)-4′-morpholinobutyrophenone |
| Sinocure® 379 | 119344-86-4 | 1-Butanone, 2-(dimethylamino)-2-(4-methylphenyl)methyl-1-4-(4-morpholinyl)phenyl- |
| Sinocure® 938 | 61358-25-6 | Bis(4-tert-butylphenyl)iodonium hexafluorophosphate |
| Sinocure® 6992 MX | 75482-18-7 & 74227-35-3 | Cationic Photoinitiator UVI-6992 |
| Sinocure® 6992 | 68156-13-8 | Diphenyl(4-phenylthio)phenylsufonium hexafluorophosphate |
| Sinocure® 6993-S | 71449-78-0 & 89452-37-9 | Mixed type triarylsulfonium hexafluoroantimonate salts |
| Sinocure® 6993-P | 71449-78-0 | 4-Thiophenyl phenyl diphenyl sulfonium hexafluoroantimonate |
| Sinocure® 1206 | Photoinitiator APi-1206 |
