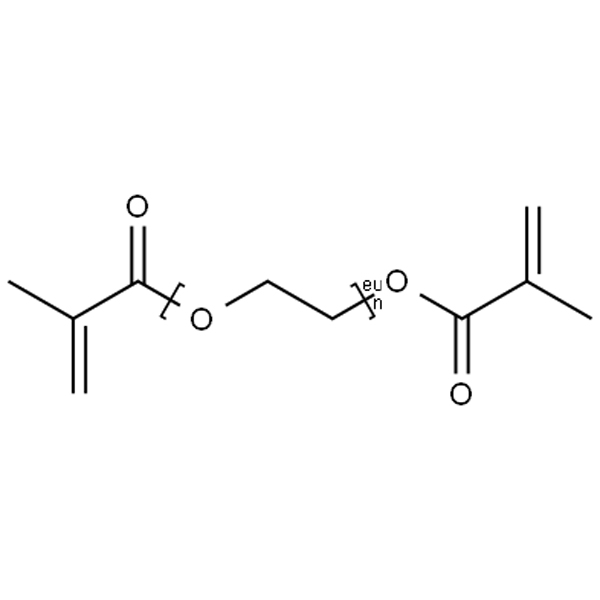
PEGDMA Monomer Application scenarios
1. Biomedical Engineering and Tissue Engineering
Hydrogel preparation, controlled drug delivery systems, tissue engineering scaffolds
Excellent biocompatibility; capable of forming hydrophilic networks via photopolymerization to carry drugs or cells.
2. Medical Devices and Therapies
Endovascular embolization for intracranial aneurysms, dental materials (e.g., surface modification, periodontal regeneration surgery)
Can be formulated into low-viscosity, injectable, photopolymerizable embolization agents; used to prepare 3D-printed dental hydrogels.
3. Industrial and Materials Science
Crosslinking agent for plastics/polymers, rubber peroxide accelerator, adhesives and sealants, electronics (e.g., photoresists)
As a bifunctional monomer, it enhances material crosslink density, heat resistance, and mechanical properties.
4. 3D Printing
3D-printed hydrogels for biomedical applications
Suitable for photopolymerization 3D printing (e.g., SLA) to fabricate hydrophilic devices with intricate structures.
💡 Application Principles and Characteristics
PEGDMA’s applicability across these diverse fields stems primarily from its core properties:
• Bifunctionality and Polymerizability: With methacrylate groups at both ends, it forms highly crosslinked 3D networks via radical polymerization (especially photopolymerization).
• Hydrophilicity and Biocompatibility: The central polyethylene glycol (PEG) segments exhibit excellent water solubility and recognized biocompatibility, minimizing immune rejection and making it highly suitable for biomedical applications.
• Tunable Properties: By adjusting the PEG segment length and polymerization conditions, the mechanical properties, swelling degree, and permeability of the final material (e.g., hydrogels) can be precisely controlled to meet diverse requirements.




Oliver White –
Fast delivery, top-notch quality. Highly impressed, will definitely be a repeat customer.