Photoinitiator CBP Application scenarios
1. Coatings and Coatings
Varnishes, wood coatings, plastic coatings, metal coatings
Used for rapid surface curing and protection, providing high gloss and abrasion resistance.
2. Inks
Offset printing inks, flexographic inks, screen printing inks
Used for printing packaging, labels, etc., enabling high-speed printing and instant drying.
3. Adhesives
UV-curable adhesives
Used for bonding electronic components, glass, and plastics, featuring fast curing and strong adhesion.
4. Electronics
Electronic component coatings, potting compounds
Provide insulation, moisture resistance, and protection.
5. Other Applications
Pharmaceutical or pesticide intermediates
Serve as raw materials for chemical synthesis.
💡 Mechanism of Action and Characteristics
Under UV light, CBP molecules absorb light energy and undergo homolytic cleavage, directly generating two active free radicals. These radicals rapidly attack double bonds in monomers (e.g., acrylic esters), initiating chain polymerization reactions that cure liquid resins into solids within seconds.
Its key features include high initiation efficiency and excellent compatibility with resins. In practical applications, it is often blended with amine co-initiators to overcome oxygen inhibition of curing and achieve more complete curing results.


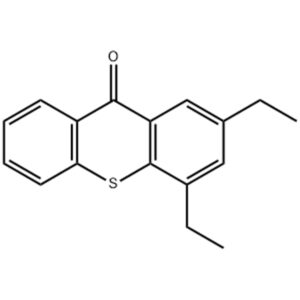



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.