BZA 모노머 적용 시나리오
1. 🔬 광학 재료
광학 렌즈, 프리즘, 도파관, 광섬유 코어/피복, 반사 방지 코팅 제조에 사용됩니다.
높은 굴절률(폴리머 굴절률 1.5 이상)을 통해 빛의 전파를 정밀하게 제어할 수 있습니다.
2. 🧬 생물의학 연구
하이드로젤(조직 공학용, 약물 서방형) 및 약물 전달체(예: 나노 입자)를 준비하는 데 사용됩니다.
생체 적합성 및 대사성을 보유하고 있으며 생체 재료 형성에 참여할 수 있습니다.
3. ⚗️ 화학 합성 및 응용
폴리 아크릴 아미드 및 폴리 아크릴산과 같은 폴리머를 합성하고, 헥 반응, 마이클 첨가 등의 유기 합성 중간체 역할을 합니다.
반응성이 높은 아크릴레이트기를 포함하고 있어 중합 및 다양한 첨가 반응이 쉽게 일어납니다.
4. 🏭 기타 산업 애플리케이션
고성능 잉크, 코팅, 접착제 및 아크릴 수지 제조에 사용됩니다.
중합 후 우수한 필름 형성 특성, 접착력 및 내구성을 제공합니다.
📝 적용 세부 사항 및 원칙
광학 애플리케이션의 핵심:
벤젠 고리 구조가 도입되어 굴절률이 높기 때문에 벤젠에서 파생된 폴리머가 빛을 보다 효과적으로 '굴절'시킬 수 있습니다. 이는 정밀한 광 경로 제어가 필요한 디바이스에 매우 중요합니다.
생물의학 애플리케이션의 현황:
현재 생체 의학 응용 분야는 주로 연구 단계에 머물러 있으며, 중합 가능한 특성을 활용하여 맞춤형 기계적 강도와 분해성을 갖춘 생체 재료를 만드는 데 초점을 맞추고 있습니다.
화학 합성에서의 역할:
다용도 모노머로서 라디칼 중합을 통해 단일 중합체를 생성하고 다른 모노머와 공중합하여 최종 폴리머의 경도, 유연성 및 기타 물리화학적 특성을 조정할 수 있습니다.

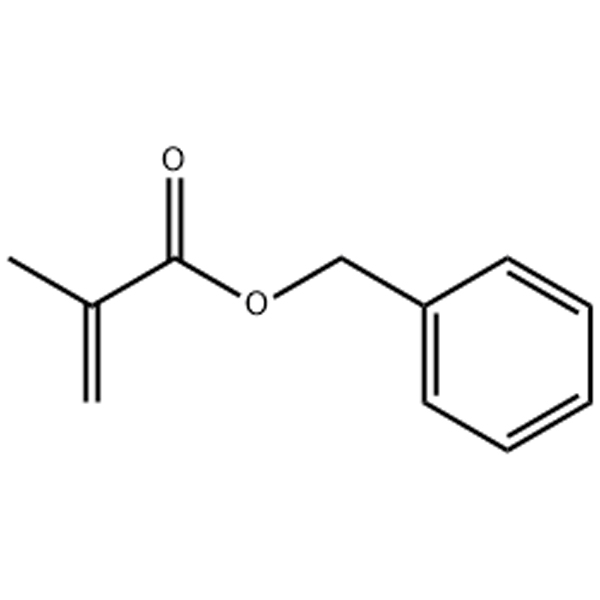




리뷰
아직 리뷰가 없습니다.