Tannase Application scenarios
1. Tea Beverage Processing
Prevents “cold turbidity,” improves extraction yield, and enhances taste and color.
Hydrolyzes the ester bonds between catechins and gallic acid in tea extract, preventing the formation of insoluble complexes (tea cream) with caffeine and thearubigins, thus clarifying the tea and reducing bitterness.
Bottled tea beverages, instant tea (e.g., the cold-water instant tea process in Japanese patent JP3951260).
2. Fruit Juice and Wine Processing
Removes astringency and clarifies the liquid.
Decomposes tannins in fruits (such as persimmons) or brewing raw materials, reducing astringency and simultaneously aiding in the precipitation of proteins and other substances, making the liquid clearer.
Persimmon de-astringency, beer clarification, wine making.
3. Animal Feed
Improves the nutritional value of feed.
Degrades anti-nutritional factors such as tannins in feed raw materials (e.g., sorghum, soybean meal), reducing the inhibition of animal digestive enzymes by tannins and improving the digestion and absorption rate of nutrients such as protein.
Processing of tannin-containing grain feed.
4. Functional Ingredient Preparation
Production of fine chemicals such as gallic acid.
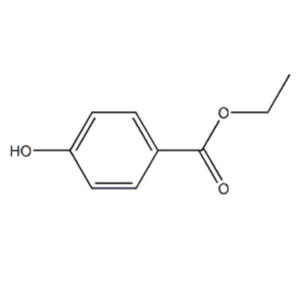
Tannase specifically hydrolyzes tannic acid to produce gallic acid and glucose. Gallic acid is an important pharmaceutical intermediate and antioxidant.
Production of basic raw materials for pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food antioxidants.
5. Other Food Processing
Improves food quality.
Applied in the processing of nuts, flour products, etc., to improve the flavor and texture of products by adjusting the tannin content.
Nut processing, baked goods, etc.