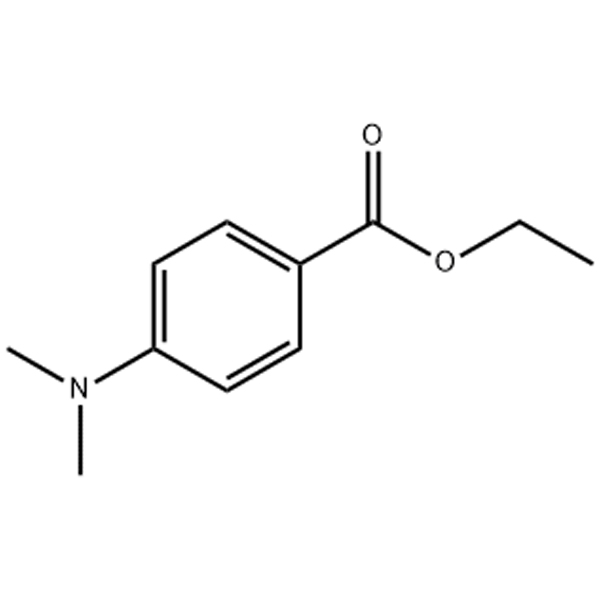
Photoinitiator EDB Application scenarios
1. UV-Curing Coatings
Wood coatings, plastic coatings, metal coatings
Used as a synergist, in combination with the main photoinitiator, to initiate the free-radical polymerization of monomers such as acrylates, achieving rapid coating curing.
2. Graphic Arts and Printing
Inks, printed electronics
Used in UV-curing inks, providing fast drying and excellent surface curing effects.
3. Adesivi
Various UV-curing adhesives
Accelerates the curing process of adhesives, improving bonding strength and production efficiency.
4. Dental Materials
Dental composite resins, adhesives
Often used in combination with camphorquinone (CQ) as a co-initiator in visible light curing systems for dental restorations.
5. Other Fields
Engineering plastics, daily chemical products, organic synthesis intermediates
Used for material modification or as a raw material for the synthesis of other compounds.
⚙️ Technical Characteristics and Mechanism of Action
The core function of EDB is as a “synergist” or “co-initiator,” and its working principle and characteristics are as follows
Effetto sinergico:
It is usually used in combination with Type II photoinitiators (such as ITX, BP, CQ). Under UV or visible light irradiation, the main initiator absorbs light energy and extracts hydrogen atoms from the EDB molecule, thereby efficiently generating active free radicals, which then initiate the polymerization reaction.
Improved Performance:
This synergistic effect effectively increases the curing speed, increases the curing depth (especially for colored systems), and reduces the problem of surface tackiness caused by oxygen inhibition.





Recensioni
Non ci sono ancora recensioni.