EMA Monomer Application scenarios
1. Coatings and Inks Industry
Architectural coatings, industrial coatings, automotive coatings, printing inks, varnishes Enhances coating flexibility, weather resistance, gloss, and adhesion.
2. Adhesives and Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives
General-purpose adhesives, pressure-sensitive tapes and labels, specialty adhesives Adjusts tackiness, cohesive strength, and drying speed to improve bonding performance on diverse substrates.
3. Plastic and Resin Modification
Acrylic (PMMA) modification, acrylic copolymer resins, engineering plastics Enhances impact resistance, processing flow, and transparency in plastics.
4. Biomedical Materials
Dental restorative materials (e.g., filling resins), orthopedic bone cements, drug-release carriers, medical catheters
Preparation of biocompatible polymers for human hard tissue repair or controlled drug delivery systems.
5. Fiber and Fabric Treatment
Fabric finishing agents, leather coating agents, paper treatment agents
Used as monomers to impart properties such as wrinkle resistance, water repellency, and softness to fibers.
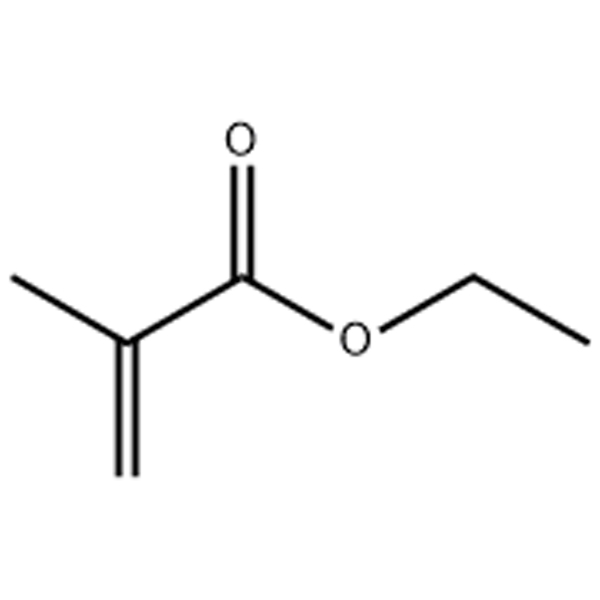
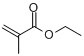
🧪 Core Reaction Principle
EMA’s defining feature is its carbon-carbon double bond, enabling radical polymerization copolymerization with other acrylic monomers (e.g., methyl methacrylate MMA). By adjusting EMA’s copolymer ratio, the glass transition temperature (Tg) of the final polymer can be precisely controlled, yielding materials ranging from soft and elastic to hard and rigid.




Christian Priestley -
Großartiger Anbieter und Dienstleistungen.