What are the applications of antioxidants, light stabilizers and the combination of both in coatings?
This paper systematically introduces the types of light stabilizers and antioxidants, studies antioxidants, light stabilizers and their application in powder coatings respectively, and describes the mechanism of their role in inhibiting or retarding the rate of light/thermal oxidation of the coating film.
With the rapid development of national economy, the application of powder coatings in outdoor is becoming more and more common. Thereby, the weatherability and durability of powder coating coating as protection and decoration are also receiving more and more attention, especially the coating film of indoor and outdoor items such as ceilings, curtain wall panels, drinking fountains, air conditioners, washing machines, aluminum profiles, etc. coating onlinecoatingol.com.
There are many factors affecting the weatherability of powder coatings, which include internal factors such as the structure and performance of resins, curing agents, color fillers, and other additives; and natural factors (external factors) such as the action of sunlight (mainly UV), the composition of the atmosphere (oxygen, ozone, industrial smoke, etc.), humidity (including acid rain, salt spray, etc.), and temperature changes.
Ultraviolet radiation is the main cause of natural aging of powder coatings, and oxygen in the atmosphere is an important factor to promote natural aging. Under the action of ultraviolet radiation and oxygen, it triggers automatic oxidation reaction of powder coating, i.e. oxidation chain reaction, which degrades powder coating. Water and heat accelerate this reaction and play a role in the promotion of photo-oxidation.
Therefore, the influence of various factors cannot be ignored. Only by understanding how various factors work on powder coatings and grasping the main contradiction can we find out the countermeasures to improve its weathering resistance.
Powder coating film in the formation process will exist weak chain bond and double-ene structure of the macromolecular chain, after the ultraviolet radiation, easy to occur light-induced oxidative degradation reaction (aging), resulting in the fading of the coating film, chalking.
In order to inhibit or retard the photo-oxidation rate of the coating film, people usually use adding antioxidants, UV absorbers or light stabilizers or a mixture of three kinds. This paper combines experiments to explore the application of antioxidants and light stabilizers in powder coatings and their effects on performance.
1. Experimental part
1.1 Preparation of test sample
The resin, curing agent, leveling agent, color filler and other additives are weighed according to the powder coating formula, put into the mixing kettle and mixed at high speed, then extruded by twin-screw extruder and cooled.
The extruded material is broken by coffee mill and then sieved through a screen, and the finished powder coating is sprayed onto the sandpaper polished steel plate by 40 kV high pressure electrostatic spraying with Jinma gun and placed in the oven for baking and curing to get the sample plate.
1.2 Performance test method
Artificial accelerated aging test: QUV was used for artificial accelerated aging test. QUV used QUB313 light source and ran for 200h, where: a value test condition: UV: 0.72W/m2, 50℃, 4h; b value test condition: condensation: 40℃, 4h.
Baking test: In order to determine the heat resistance of the light stabilizer, the oven baking method was used, and the baking conditions were 220℃ and 30min for heat resistance test.
2、Results and discussion
2.1 Application study of antioxidants
From the mechanism of thermal oxygen degradation of polymers, it is known that the thermal oxygen degradation of polymers is mainly caused by the occurrence of chain-linked radical reactions triggered by the generation of free radicals from hydroperoxides by heat.
Therefore, the thermal oxygen degradation of polymers can be inhibited by radical trapping and hydroperoxide decomposition, as shown in Figure 1. Among them, antioxidants are widely used for the above inhibition of oxidation.
Antioxidants (or heat stabilizers) are additives that are used to inhibit or delay the degradation of polymers by the action of oxygen or ozone in the atmosphere, and are the most widely used additives in polymer materials.
Powder coatings are subject to thermal oxygen degradation after baking at high temperatures or sunlight, aging, yellowing and other phenomena seriously affect the appearance and performance of the product, in order to prevent or reduce the occurrence of this trend, usually using the addition of antioxidants or heat stabilizers to achieve.
Antioxidants can be divided into three main categories according to their function (i.e., the intervention behavior of the automatic oxidation chemical process).
The first category is called chain-terminating antioxidants, which mainly capture or scavenge free radicals generated by the auto-oxidation of polymers.
The second category is called hydroperoxide decomposer-type antioxidants, mainly to induce non-radical-type decomposition of hydroperoxides in polymers.
The third category is called metal ion passivator-type antioxidants, which can form a stable chelate with harmful metal ions, thereby blunting the catalytic effect of metal ions on the polymer auto-oxidation process.
The first of the three types of antioxidants is called the main antioxidant, mainly phenol blockers, seco-aromatic amines; the second and third categories are called auxiliary antioxidants, phosphite, dithiocarbamate metal salts, etc.. In order to obtain a stable coating to meet the application requirements, usually to choose a variety of antioxidant compounding.
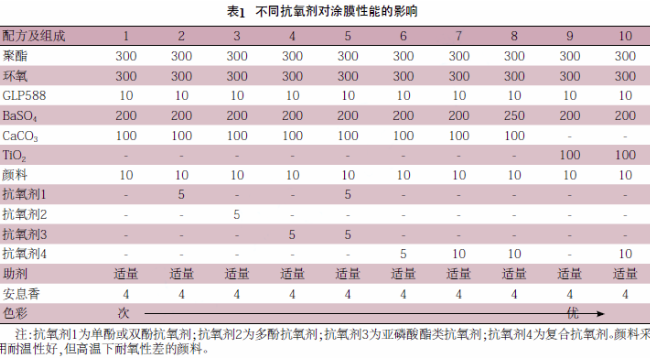
The following test uses different antioxidant compounding added to the powder coating formulation, after spraying and curing, the sample is made, and the b value is measured in the same film thickness with color difference meter, and the color of the coating film is evaluated using the international common powder CIE Lab color system (DIN 6174, ISO 10526 and ASTM 2244).
Table 1 shows the test results after sorting the color of the coated film from sub-increasing to excellent, it can be seen that.
(1) The basic formulation 1 shows serious loss of light, although the pigment has better heat resistance, but the color change occurs after film formation, and the analysis is that the pigment is oxidized at high temperature, and some groups within the pigment react under the action of oxygen.
(2) The color change of formula 2 and formula 3 is better than formula 1, but the improvement is not obvious, and formula 3 has better effect than formula 2.
After analysis, the antioxidant prevented further oxidation and made the color change less, and the effect of antioxidant 3 was better than that of antioxidant 2. Another reason may be due to the fact that both are hindered amines to prevent the production of dyeing groups after oxidation of pigments, but the effect is not good and can only prevent further reaction after partial oxidation, so the effect is not optimal.
(3) Formulation 4 is better than formulation 3, but not optimal. Because the phosphite antioxidant has good color protection ability, it has reducing property, which can make the pigment oxidized at high temperature to restore quickly, so it has better antioxidant effect.
(4) The effect achieved by formulation 5 is better than formulation 4. The main antioxidant and auxiliary antioxidant are used together in this formula, so that the further oxidation of the pigment is prevented and the oxidized group is rapidly reduced, and the auxiliary antioxidant can make the dye group produced by the main antioxidant lighter, which has good synergistic effect.
(5) Formulation 6, which used a compound antioxidant, had significantly better color retention than formulation 5. Antioxidant 4 was a mixture of high efficiency phosphite and phenolic antioxidants, and they were properly proportioned to have a good antioxidant effect.
(6) Formulation 7 is better than formulation 6, and the color effect is basically the same as the original pigment. The recommended dosage of antioxidant is 0.5% to 1.0%, so the dosage of formulation 6 is significantly less. It shows that the color effect is maintained better after the dosage of compound antioxidant is increased.
(7) Formulation 8 test shows that the use of antioxidants can effectively inhibit the oxidative degradation of the resin in the process and improve the impact resistance during extrusion and film curing in powder coating powder making.
The formulation when adding antioxidants can increase the color-base ratio to achieve the same performance without the addition of antioxidants when the smaller color-base ratio. This is because the addition of antioxidants reduces the tendency of resin decomposition into low molecular weight products, so that large molecule resins better encapsulate more fillers, while the performance remains unchanged.
(8) Formulation 10 and Formulation 9 white coating film samples can be seen in the addition of antioxidants can effectively inhibit the processing of powder coatings and post-curing process yellowing, improve the color performance of white powder coatings.
The above test results show that although there are many factors affecting the appearance of oxidation in the coating film, such as the quality and type of resin, pigment, additives, formulation design of the coating, production process, temperature, atmosphere, humidity and other natural factors, the application of suitable antioxidants does reduce the occurrence of this trend.
2.2 Application study of light stabilizers
The degradation of polymers under the action of light and oxygen is called “photo-oxidative degradation”. Light stabilizers, also known as UV stabilizers, are a class of stabilization additives used to inhibit the photo-oxidative degradation of polymer resins and improve the weatherability of powder coating films.
According to the different stabilization mechanisms, light stabilizers can be divided into light shielding agents, UV absorbers, excited state bursting agents and free radical capture agents.
Due to the diversity and complexity of powder coating formulation, curing process and curing form, it makes the light conservation and light protection of powder coating very important.
Secondly, light stabilizer is very effective for light aging of coating and prolonging the service life of coating film, and the amount is very small, generally only 0.5%~1.0% of the total formulation.
Therefore, the application of light stabilizers in powder coatings to improve their weathering properties is a very simple, low-cost and very effective method. Table 2 and Table 3 will help to illustrate the effect of light stabilizers on the performance of the coating film.
Based on the formulation in Table 2, the light stabilizer was added to the coating, and the coating film samples were cured by spraying, and the internationally popular rapid weathering test evaluation method – artificial accelerated aging (QUV) test and baking test were used.
Through the test results in Table 3, the application performance of the light stabilizer is evaluated as follows.
(1) indoor powder weatherability is very poor, but the addition of light stabilizers will play a significant role.
(2) A and D formulations are not added to the light stabilizer, the test shows that both significantly worse than the sample added to the light stabilizer.
(3) Formulations C and F showed that the increased amount of light stabilizer had a significant improvement on the light and color retention of the coating film.
(4) The baking test results show that the light stabilizer has no temperature resistance, and the temperature resistance of the coating film should be solved by adding anti-yellowing additives.
2.3 Research on the synergistic application of antioxidants and light stabilizers
Through the above test, we can understand that the aging of the coating film is actually the result of the joint action of UV light and oxygen, and this process includes two different processes of photodegradation and photo-oxidation.
However, light stabilizers and antioxidants have different stabilization mechanisms on the coating film, and the combination of two stabilizers with different mechanisms of action is expected to achieve better stabilization effect than a single stabilizer, i.e. synergistic effect.
Currently there are such stabilizers on the market, which is also a development trend of stabilizers. But the synergistic effect at the same time, two different stabilizers between the additive and antagonistic effect will also appear.
Therefore, in the antioxidant and light stabilizer with a good understanding of the different reactions between the two is critical, only to master the effect of the two with the potential chemical reactions, in order to design an effective antioxidant and light stabilizer with the system.
The most typical ones are HALS and antioxidants, UV absorbers and antioxidants and UV shielding agents and antioxidants and so on.
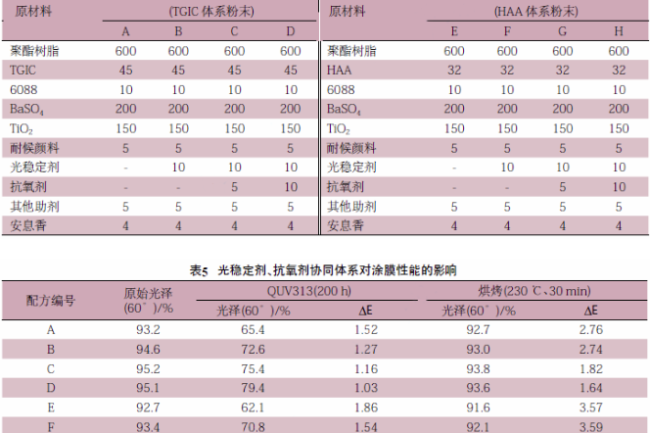
Through accelerated aging and baking tests on the coating film, the effect of adding antioxidants and light stabilizers to the powder coating formulation was evaluated. The test formulations and results are shown in Table 4 and Table 5.
Through the test results, the light stabilizer is evaluated.
(1) The addition of light stabilizer will play a significant role in the weathering resistance of the powder, but there is no change in the yellowing resistance of the coating film.
(2) Light stabilizer and antioxidant with the coating film weathering resistance and discoloration has a significant effect, and the amount of both 1:1 when the best.
(3) Light stabilizer and antioxidant have better effect in HAA system.
The use of light stabilizers and antioxidants is not so simple as introduced in the article. The effect of using different light stabilizers with antioxidants needs to be confirmed by further experiments based on theory.
For example, the use of HALS-type light stabilizers and sulfur-containing antioxidants will produce antagonistic effects and degrade the performance of the polymer; the use of HALS and phosphorus-containing polymers should ensure the best synergy at a concentration of 1:1; the use of low molecular weight HALS and only additive effects, while the use of high molecular weight HALS and low molecular weight HALS has a synergistic effect, etc.
3、Conclusion
The addition of antioxidant and light stabilizer to powder coatings can effectively inhibit and reduce the speed of thermal oxidation and photo-oxidation of polymer macromolecules in the production and application of powder coatings, significantly improve the heat and light resistance of the coating film, delay the degradation and aging process of the coating film, and prolong the service life of the coating film.
Light stabilizers and antioxidants used in high-performance powder coatings, if used properly, there will be a synergistic effect, significantly improve the weathering properties of the powder coating film, especially Super-Duable powder coating film.
If used improperly, there will be an additive effect, or even an antagonistic effect, which makes the stability of the coating film decrease.
The trend of stabilizers and will be developed in the direction of multi-functionality.